Welcome to the comprehensive guide to air mass worksheet answer key PDF, where we delve into the fascinating world of air masses, their properties, movement, and impact on weather patterns. This guide is meticulously crafted to provide a thorough understanding of air mass dynamics, equipping you with the knowledge to unravel the mysteries of the atmosphere.
As we journey through this guide, we will explore the diverse types of air masses, their origins, and their distinct characteristics. We will unravel the intricate interplay between air mass properties, such as temperature, humidity, and stability, and their influence on weather conditions.
Furthermore, we will trace the factors that govern air mass movement, shedding light on their interactions with each other and the Earth’s surface.
Air Mass Classification
Air masses are large bodies of air that have relatively uniform temperature and humidity characteristics. They are classified based on their source region and temperature characteristics.
| Air Mass Type | Abbreviation | Source Region | Temperature Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continental Arctic | cA | High-latitude continental regions | Very cold |
| Continental Polar | cP | Mid-latitude continental regions | Cold |
| Continental Tropical | cT | Low-latitude continental regions | Warm |
| Maritime Arctic | mA | High-latitude oceanic regions | Cold and moist |
| Maritime Polar | mP | Mid-latitude oceanic regions | Cool and moist |
| Maritime Tropical | mT | Low-latitude oceanic regions | Warm and moist |
Air Mass Properties
Air masses have several important properties, including temperature, humidity, and stability. Temperature refers to the warmth or coldness of the air mass. Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor in the air mass. Stability refers to the ability of the air mass to resist vertical movement.
These properties influence weather conditions. For example, cold air masses can bring cold temperatures and precipitation, while warm air masses can bring warm temperatures and humidity.
Air Mass Movement
Air masses move in response to pressure gradients. Pressure gradients are created by differences in air pressure. Air flows from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure.
The movement of air masses is also influenced by the Coriolis effect. The Coriolis effect is a deflection of moving objects due to the Earth’s rotation. In the Northern Hemisphere, the Coriolis effect deflects air masses to the right, while in the Southern Hemisphere, it deflects air masses to the left.
Air masses interact with each other and with the Earth’s surface. When two air masses with different temperatures meet, they can create a front. Fronts are boundaries between air masses that can cause weather conditions such as precipitation and thunderstorms.
Air Mass Weather Patterns
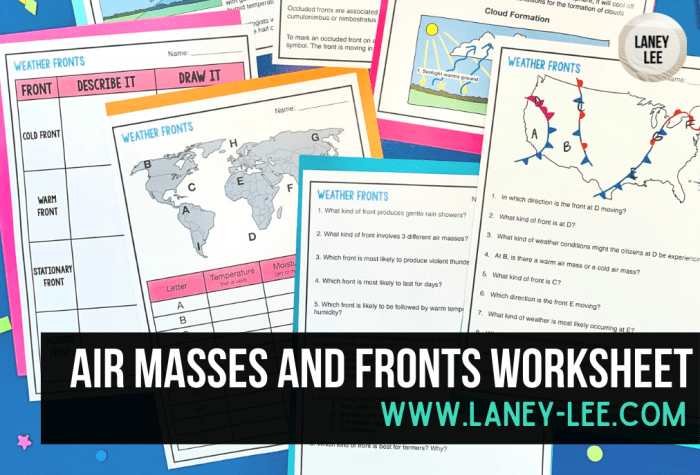
Air masses are associated with different types of weather patterns. For example, continental Arctic air masses can bring cold and dry weather, while maritime tropical air masses can bring warm and humid weather.
Air masses can also influence precipitation. Cold air masses can cause precipitation in the form of snow or sleet, while warm air masses can cause precipitation in the form of rain or thunderstorms.
Air Mass Modification
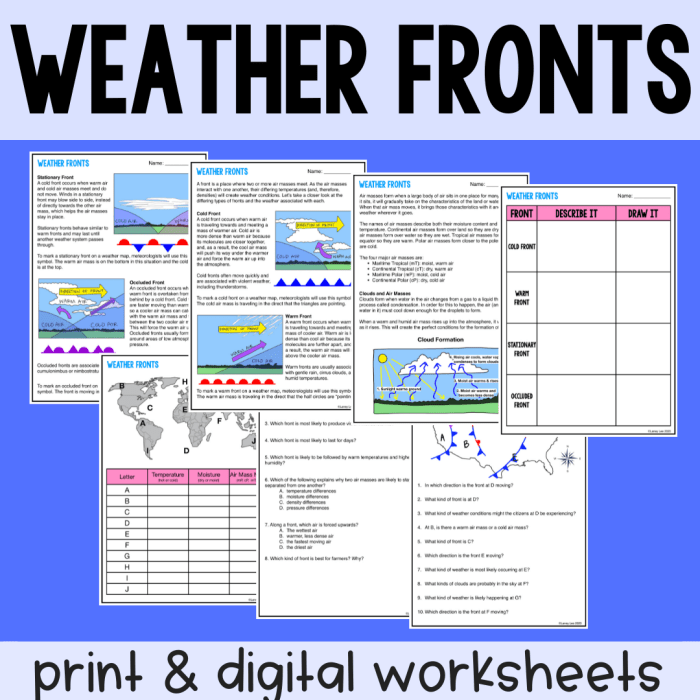
Air masses can be modified as they move across the Earth’s surface. Modification can occur through heating, cooling, or moisture addition or removal.
Heating can occur when an air mass moves over a warm surface, such as the ocean. Cooling can occur when an air mass moves over a cold surface, such as a snow-covered area.
Moisture addition can occur when an air mass moves over a moist surface, such as a body of water. Moisture removal can occur when an air mass moves over a dry surface, such as a desert.
Modification can affect the properties and behavior of air masses. For example, heating can make an air mass warmer and less stable, while cooling can make an air mass colder and more stable.
Top FAQs: Air Mass Worksheet Answer Key Pdf
What is an air mass?
An air mass is a large body of air with relatively uniform temperature and humidity characteristics that covers a vast region of the Earth’s surface.
How do air masses form?
Air masses form over regions with similar surface characteristics, such as oceans, deserts, or ice caps. The air in these regions takes on the temperature and humidity properties of the surface below.
What are the different types of air masses?
Air masses are classified based on their source region and temperature characteristics. The main types include continental (c), maritime (m), tropical (T), polar (P), and arctic (A).
How do air masses affect weather patterns?
Air masses play a significant role in shaping weather patterns. Different air masses bring with them their own unique temperature, humidity, and stability characteristics, which can influence precipitation, temperature, and wind conditions.