Classify these substances as molecular or ionic: an intriguing topic that delves into the fundamental nature of matter. By examining the key characteristics and properties of these substances, we gain a deeper understanding of their behavior and applications in various fields.
This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of molecular and ionic substances, their properties, classification, and real-world applications. Dive into the fascinating world of chemistry and unravel the mysteries surrounding these substances.
Definition of Molecular and Ionic Substances: Classify These Substances As Molecular Or Ionic
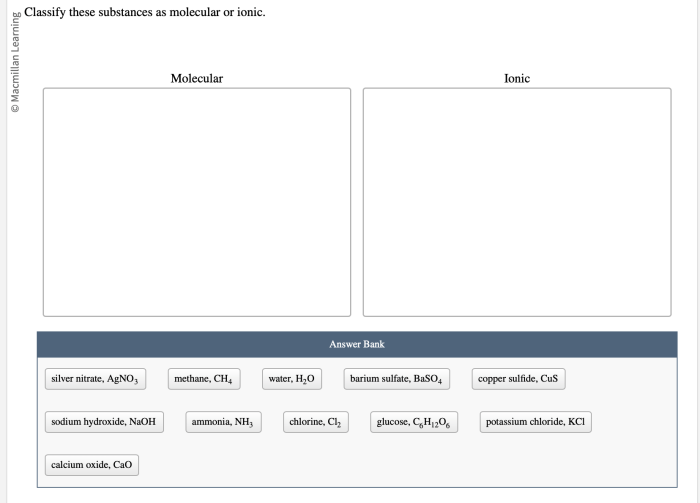
Chemical substances can be classified into two broad categories: molecular substances and ionic substances. These categories are based on the fundamental differences in their chemical structures and properties.
Molecular Substances
Molecular substances are composed of molecules, which are electrically neutral groups of atoms held together by covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons, resulting in a stable electronic configuration.
Molecular substances typically have low melting and boiling points, as the intermolecular forces between molecules are relatively weak. They are generally poor conductors of electricity and are often soluble in nonpolar solvents.
Ionic Substances, Classify these substances as molecular or ionic
Ionic substances are composed of ions, which are charged particles formed when atoms gain or lose electrons. The electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions forms ionic bonds, resulting in a crystal lattice structure.
Ionic substances typically have high melting and boiling points, as the electrostatic forces between ions are strong. They are good conductors of electricity when dissolved in water or melted and are generally soluble in polar solvents.
Properties of Molecular and Ionic Substances
The properties of molecular and ionic substances differ significantly due to their distinct chemical structures and bonding.
Physical Properties
Molecular Substances:
- Low melting and boiling points
- Poor conductors of electricity
- Soluble in nonpolar solvents
Ionic Substances:
- High melting and boiling points
- Good conductors of electricity (when dissolved or melted)
- Soluble in polar solvents
Chemical Properties
Molecular Substances:
- Low reactivity
- Nonpolar or slightly polar
Ionic Substances:
- High reactivity
- Highly polar or ionic
Classification of Substances
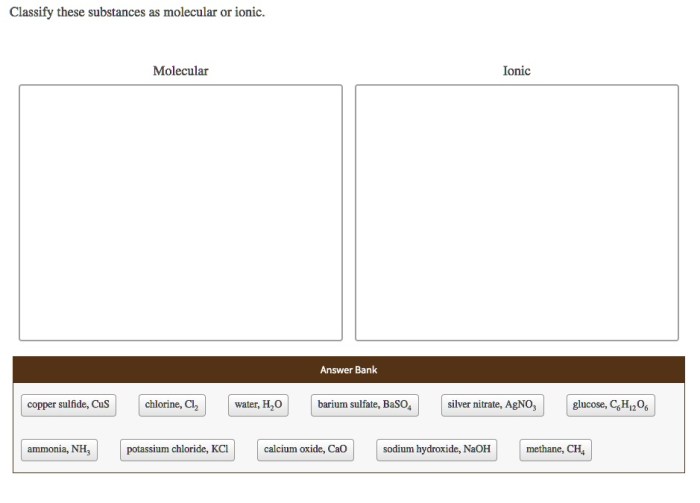
| Molecular Substances | Ionic Substances |
|---|---|
| Water (H2O) | Sodium chloride (NaCl) |
| Sugar (C12H22O11) | Potassium iodide (KI) |
| Carbon dioxide (CO2) | Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) |
Reasoning:Molecular substances are composed of molecules and have covalent bonds, while ionic substances are composed of ions and have ionic bonds.
Applications of Molecular and Ionic Substances

The properties of molecular and ionic substances make them suitable for various applications in everyday life.
Molecular Substances
- Water:Essential for life, used as a solvent, coolant, and cleaning agent
- Sugar:Provides energy, used as a sweetener in food and beverages
- Carbon dioxide:Used in fire extinguishers, carbonated beverages, and as a refrigerant
Ionic Substances, Classify these substances as molecular or ionic
- Table salt (NaCl):Seasoning, food preservative
- Baking soda (NaHCO3): Leavening agent in baking, odor neutralizer
- Calcium carbonate (CaCO3): Antacid, construction materials, fertilizer
Common Queries
What is the key difference between molecular and ionic substances?
Molecular substances are composed of molecules held together by covalent bonds, while ionic substances are composed of ions held together by electrostatic forces.
How can I determine if a substance is molecular or ionic?
Generally, substances formed between metal and nonmetal elements are ionic, while substances formed between nonmetal elements are molecular.
What are some examples of molecular and ionic substances?
Examples of molecular substances include water (H2O), sugar (C12H22O11), and methane (CH4). Examples of ionic substances include sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium iodide (KI), and calcium oxide (CaO).