A model rocket blasts off from the ground rising straight, embarking on a captivating journey that unveils the intricate world of rocket propulsion, design, and trajectory. From the fundamental principles of physics to the innovative applications of model rocketry, this exploration delves into the science, history, and educational value of these fascinating devices.
As a model rocket ascends, it harnesses the power of rocket propulsion, a concept rooted in Newton’s third law of motion. The rocket’s engine expels exhaust gases downward, generating an equal and opposite force that propels the rocket upward. This fundamental principle forms the foundation of rocketry, enabling the exploration of space and countless other applications.
1. Rocket Propulsion
Rocket propulsion is based on the principle of Newton’s third law of motion, which states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. In a rocket, the action is the expulsion of mass (propellant) out of the engine nozzle.
The reaction is the thrust that propels the rocket forward.
There are various types of rocket engines, each with its characteristics. Solid-propellant rockets are simple and reliable, using a solid propellant that burns to produce hot gases. Liquid-propellant rockets offer greater control and efficiency, using a liquid propellant that is injected into the combustion chamber and mixed with an oxidizer.
Different Types of Rocket Engines, A model rocket blasts off from the ground rising straight
- Solid-propellant rockets
- Liquid-propellant rockets
- Hybrid rockets
- Ion rockets
2. Rocket Design and Structure: A Model Rocket Blasts Off From The Ground Rising Straight

A model rocket consists of several components, each serving a specific function. The nose cone, located at the front of the rocket, reduces air resistance and helps stabilize the rocket during flight. The body tube provides the main structure and houses the engine and other components.
Fins are attached to the body tube to provide stability and control during flight. They help steer the rocket and prevent it from tumbling. The engine, located at the base of the rocket, generates the thrust that propels the rocket upward.
Importance of Weight Distribution and Aerodynamics
Weight distribution and aerodynamics play a crucial role in rocket design. The rocket must be balanced so that its center of gravity is in the correct position for stable flight. The rocket’s shape and surface area affect its aerodynamic properties, influencing its stability and efficiency.
3. Rocket Launch Trajectory
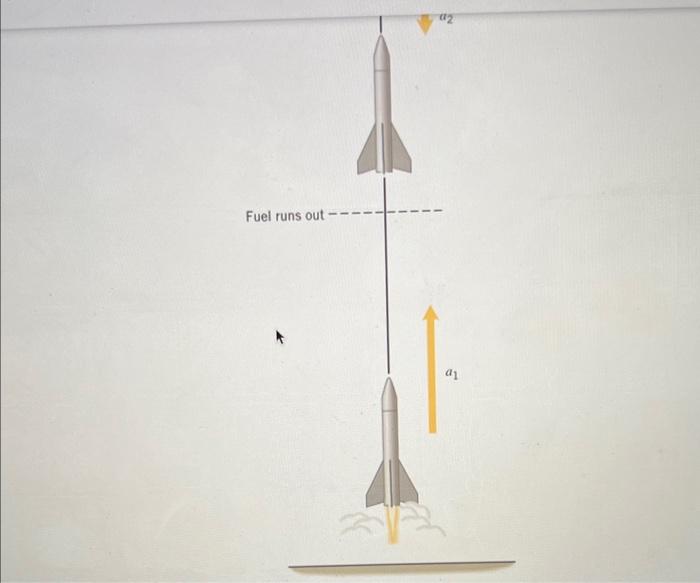
The trajectory of a model rocket is influenced by several factors, including the initial launch angle, thrust, air resistance, and gravity. After launch, the rocket follows a parabolic path, reaching a maximum altitude before descending back to the ground.
The initial launch angle determines the rocket’s range. A higher launch angle results in a longer range, while a lower launch angle results in a shorter range. Air resistance acts against the rocket’s motion, slowing it down and reducing its altitude and range.
Role of Air Resistance and Gravity
Gravity pulls the rocket back towards the ground, causing it to descend. The combined effects of air resistance and gravity shape the rocket’s trajectory and determine its flight path.
4. Rocket Recovery Systems

Model rockets are typically equipped with recovery systems to retrieve them after launch. The most common recovery system is a parachute, which is deployed after the rocket reaches its peak altitude.
The parachute slows down the rocket’s descent and allows it to land safely. Other recovery systems include streamer ribbons, which are lightweight and provide less drag than parachutes, and drogue parachutes, which are small parachutes used to stabilize the rocket during descent.
Importance of a Stable Descent and Minimizing Damage
A stable descent is crucial to minimize damage to the rocket upon landing. Parachutes and other recovery systems help slow down the rocket’s descent and prevent it from crashing into the ground.
Top FAQs
What is the purpose of a model rocket?
Model rockets serve multiple purposes, including educational, recreational, and research applications. They are used to teach STEM principles, explore aerodynamics, and provide hands-on experience with rocketry.
How high can a model rocket fly?
The altitude reached by a model rocket depends on several factors, such as the engine power, rocket design, and environmental conditions. Some high-power model rockets can reach altitudes of several thousand feet.
Is model rocketry safe?
Model rocketry can be a safe and enjoyable activity when proper safety precautions are followed. It is crucial to select a suitable launch site, follow launch guidelines, and ensure that all participants maintain a safe distance from the launch area.