Kolb’s model divides people into either reflective or active learners, introducing a foundational concept in educational psychology that has shaped our understanding of how individuals acquire knowledge and skills. This model proposes that learners possess distinct preferences and approaches to the learning process, with each type exhibiting unique strengths and weaknesses.
By exploring the characteristics, behaviors, and implications of reflective and active learning styles, we gain valuable insights into effective teaching practices and personalized learning experiences.
Introduction: Kolb’s Model Divides People Into Either Reflective Or Active Learners
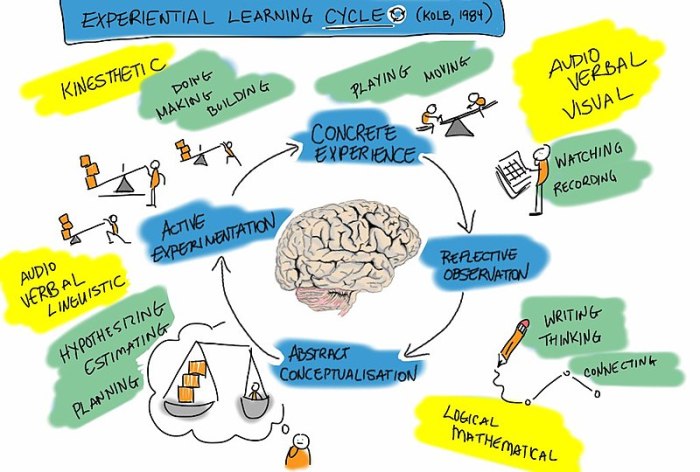
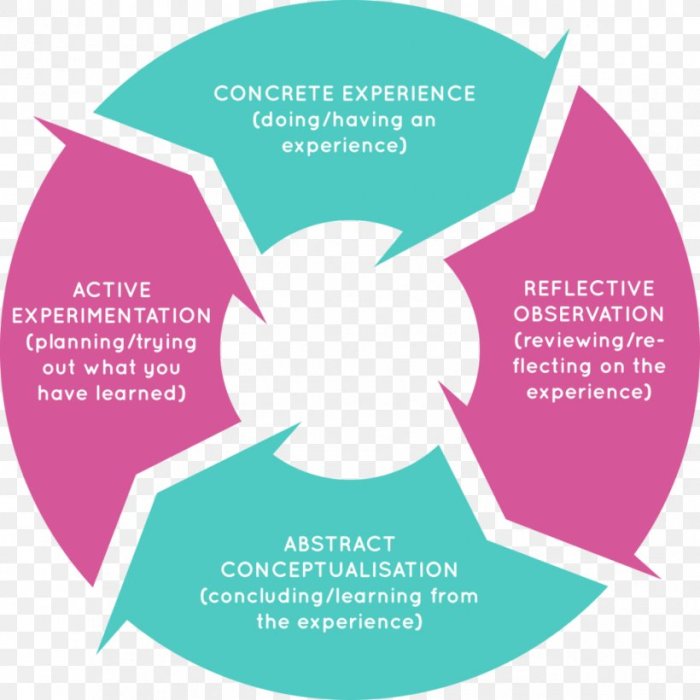
Kolb’s learning cycle is a model of experiential learning that suggests that people learn best by doing, reflecting, thinking, and applying their experiences. Kolb identified two main types of learners: reflective and active.
Reflective Learners
Reflective learners prefer to learn by observing and thinking about their experiences. They are often introverted and prefer to work independently. They learn best by reading, writing, and listening to lectures.
- Strengths:
- Analytical
- Good at problem-solving
- Able to see the big picture
- Weaknesses:
- Can be slow to learn
- May not be able to apply their knowledge to real-world situations
- May be too focused on theory
Active Learners
Active learners prefer to learn by doing and experiencing. They are often extroverted and prefer to work in groups. They learn best by doing projects, simulations, and role-playing.
- Strengths:
- Practical
- Good at problem-solving
- Able to apply their knowledge to real-world situations
- Weaknesses:
- Can be impulsive
- May not be able to see the big picture
- May be too focused on the details
Comparison of Reflective and Active Learners
| Characteristic | Reflective Learners | Active Learners |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Preferences | Observing, thinking | Doing, experiencing |
| Behaviors | Introverted, independent | Extroverted, group-oriented |
| Strengths | Analytical, problem-solving, big picture | Practical, problem-solving, real-world application |
| Weaknesses | Slow to learn, theory-focused | Impulsive, details-focused |
FAQ Guide
What are the key characteristics of reflective learners?
Reflective learners prefer to observe, analyze, and contemplate information before taking action. They are introspective, enjoy written assignments, and value feedback.
How do active learners differ from reflective learners?
Active learners are hands-on, experiential learners who prefer to engage in practical activities and simulations. They are outgoing, enjoy group projects, and learn best by doing.
What are the limitations of Kolb’s model?
Kolb’s model is a simplified representation of learning styles and may not fully capture the complexity of individual learning preferences. It also does not account for cultural or situational factors that can influence learning.