An 80 kg construction worker sits down, and a multitude of forces come into play. Understanding the biomechanics of sitting is crucial for preventing musculoskeletal disorders and promoting overall well-being.
This comprehensive analysis delves into the pressure distribution on the worker’s buttocks and thighs, the role of muscles and ligaments in supporting the body, and the potential health risks associated with prolonged sitting. Furthermore, it explores innovative engineering solutions and ergonomic principles to optimize sitting posture and enhance comfort.
Biomechanics of Sitting: An 80 Kg Construction Worker Sits Down

When an 80 kg construction worker sits down, several forces act on their body. The force of gravity pulls them downward, while the chair exerts an upward force to support their weight. This results in a distribution of pressure on the worker’s buttocks and thighs.
Pressure Distribution
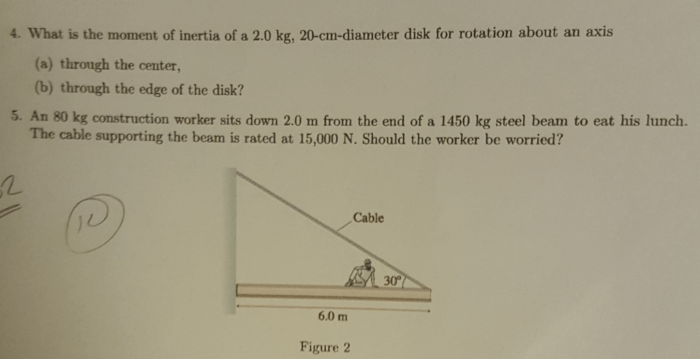
The pressure distribution on the worker’s buttocks is highest at the ischial tuberosities, which are the two bony prominences at the base of the pelvis. The pressure on the thighs is highest at the greater trochanters, which are the large bony protrusions at the top of the femur.
Muscles and Ligaments
The muscles and ligaments of the lower body work together to support the body during sitting. The gluteal muscles, which are located in the buttocks, help to extend the hip joint and prevent the worker from slouching. The hamstrings, which are located at the back of the thighs, help to flex the knee joint and prevent the worker from sliding forward in the chair.
Ergonomics of Sitting

An ergonomic workstation can help to minimize the risk of musculoskeletal disorders for construction workers who sit for extended periods.
Chair Selection
The chair should be adjustable in height and have a supportive backrest. The seat should be firm enough to provide support, but not so firm that it causes discomfort.
Desk Height
The desk should be high enough so that the worker’s elbows are bent at a 90-degree angle when they are typing. The monitor should be positioned so that the top of the screen is at eye level.
Posture and Movement Breaks
It is important for workers to maintain good posture while sitting. They should sit up straight with their shoulders relaxed and their feet flat on the floor. Workers should also take regular movement breaks to help prevent muscle fatigue and stiffness.
Health Implications of Sitting
Prolonged sitting has been linked to a number of health risks, including obesity, cardiovascular disease, and musculoskeletal disorders.
Obesity
Sitting for long periods of time can lead to weight gain, as it reduces the number of calories that the body burns. This can increase the risk of obesity, which is a major risk factor for a number of chronic diseases.
Cardiovascular Disease
Sitting for long periods of time can also increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. This is because sitting reduces the blood flow to the legs, which can lead to the formation of blood clots. Blood clots can travel to the heart and lungs, causing a heart attack or stroke.
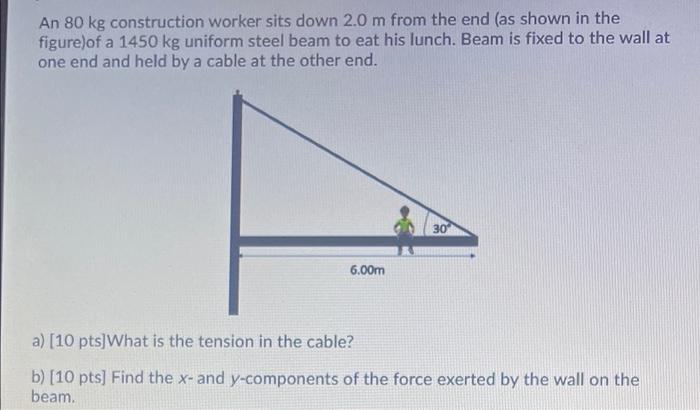
Musculoskeletal Disorders, An 80 kg construction worker sits down
Sitting for long periods of time can also lead to musculoskeletal disorders, such as back pain, neck pain, and carpal tunnel syndrome. This is because sitting puts stress on the muscles and ligaments of the back, neck, and arms.
Engineering Solutions for Sitting
A number of engineering solutions can be used to improve the comfort and support of sitting surfaces.
Wearable Devices
Wearable devices can be used to monitor the sitting posture of workers and provide feedback to help them improve their posture.
Innovative Materials
Innovative materials can be used to create sitting surfaces that are more comfortable and supportive. For example, memory foam can be used to create cushions that conform to the shape of the body, providing better support.
Smart Furniture
Smart furniture can be used to automatically adjust to the body and posture of the worker. This can help to improve comfort and support, and reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders.
General Inquiries
What are the potential health risks of prolonged sitting for an 80 kg construction worker?
Prolonged sitting can increase the risk of obesity, cardiovascular disease, and musculoskeletal disorders, such as back pain and neck pain.
How can an ergonomic workstation minimize the risk of musculoskeletal disorders for an 80 kg construction worker who sits for extended periods?
An ergonomic workstation should include a chair with good lumbar support, a desk of appropriate height, and a monitor placed at eye level. Regular movement breaks are also essential.
What are some innovative engineering solutions for improving the comfort and support of sitting surfaces?
Innovative engineering solutions include the use of pressure-sensitive materials, adjustable seat cushions, and smart furniture that automatically adjusts to the worker’s body and posture.