Delving into the intricacies of life, the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells POGIL answer key serves as a roadmap to understanding the fundamental distinctions between these two cell types. This comprehensive guide illuminates the presence or absence of a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, unraveling the variations in cell size and complexity that shape the diversity of life on Earth.
Through a detailed exploration of cell structures and functions, the answer key meticulously compares the roles of key organelles in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Ribosomes, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus take center stage, revealing their specific contributions to cell function.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Key Differences
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are two distinct types of cells that exhibit fundamental differences in their structure, organization, and complexity. These differences have significant implications for their function and evolutionary history.
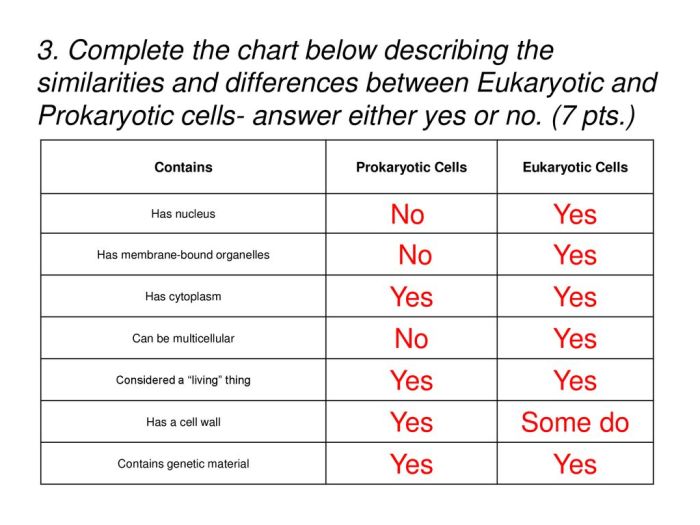
The most striking difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is the presence or absence of a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus and instead have a nucleoid region where their DNA is concentrated. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, possess a well-defined nucleus enclosed by a nuclear membrane.
Another key difference is the presence of membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cells. Organelles are specialized structures that perform specific functions within the cell. Prokaryotic cells typically lack membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells possess a variety of organelles, including mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.
Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller and less complex than eukaryotic cells. They typically range in size from 0.1 to 5 micrometers, while eukaryotic cells can range from 10 to 100 micrometers or more. The increased size and complexity of eukaryotic cells allow for greater specialization and compartmentalization of functions.
Cell Structures and Functions, Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells pogil answer key
| Organelle | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Ribosomes | Present, free in cytoplasm | Present, free in cytoplasm and bound to endoplasmic reticulum |
| Mitochondria | Absent | Present, site of cellular respiration |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Absent | Present, involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism |
| Golgi Apparatus | Absent | Present, involved in protein modification and secretion |
Cell Division Processes
Cell division is the process by which cells reproduce. Prokaryotic cells undergo binary fission, a simple process in which the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Eukaryotic cells undergo more complex processes of cell division, including mitosis and meiosis.
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Mitosis occurs during growth, development, and repair of tissues. Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that occurs in reproductive cells and results in the production of haploid gametes (eggs or sperm).
The key differences between binary fission and mitosis are the presence of a mitotic spindle in mitosis and the halving of the chromosome number in meiosis.
Evolutionary Implications
The differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have significant evolutionary implications. The endosymbiotic theory proposes that eukaryotic cells evolved from a symbiotic relationship between a prokaryotic cell and an aerobic bacterium. This theory suggests that the mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells were once free-living bacteria that were engulfed by a larger prokaryotic cell.
The endosymbiotic theory is supported by several lines of evidence, including the presence of DNA in mitochondria and chloroplasts, the similarity of their ribosomes to those of prokaryotes, and the fact that mitochondria and chloroplasts can divide independently of the rest of the cell.
The endosymbiotic theory has helped to explain the origin of eukaryotic cells and the diversity of life on Earth. It suggests that the evolution of eukaryotic cells was a major turning point in the history of life, leading to the development of more complex and specialized organisms.
FAQ Compilation: Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Pogil Answer Key
What is the primary difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells possess these structures.
How do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells divide?
Prokaryotic cells undergo binary fission, while eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis and meiosis.
What is the evolutionary significance of the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
The endosymbiotic theory suggests that eukaryotic cells evolved from the engulfment of prokaryotic cells by larger cells.